|
MANDELIC ACID
| ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 90-64-2 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 202-007-6, 210-277-1 | |
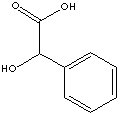
| FORMULA | C6H5CHOHCOOH | |
| MOL WT. | 152.15 | |
| H.S. CODE | 2918.19.1200 | |
|
TOXICITY |
||
| SYNONYMS | alpha-hydroxybenzeneacetic acid; (RS)-Mandelic acid; | |
| alpha-Hydroxyphenylacetic acid; Amygdalic acid; DL-Amygdalic Acid; Uromaline; -Hydroy-2-phenylacetic acid; 2-Phenyl-2-hydroxyacetic acid; 2-Phenylglycolic acid; Acido mandelico; DL-Hydroxy(phenyl)acetic acid; | ||
|
SMILES |
c1([C@@H](C(O)=O)O)ccccc1 | |
|
CLASSIFICATION |
||
|
EXTRA NOTES |
Other RN: 611-72-3, 15769-78-5, 71036-61-8, 114-21-6 (hydrochloride), 134-95-2 (calcium salt), 530-31-4 (ammonium salt) | |
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | ||
| PHYSICAL STATE |
White crystalline flakes | |
| MELTING POINT |
118 - 121 C | |
| BOILING POINT |
| |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | ||
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | Soluble | |
| pH | ||
| VAPOR DENSITY | ||
|
AUTOIGNITION |
| |
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
| |
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 2; Flammability: 0; Reactivity: 0 | |
| FLASH POINT |
| |
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions | |
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS | ||
|
USA.gov - Mandelic acid Wikipedia Linking - Mandelic acid Google Scholar Search - Mandelic acid U.S. National Library of Medicine - Mandelic acid PubChem Compound Summary - Mandelic acid Drug Bank - Mandelic acid KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) - Mandelic acid http://www.ebi.ac.uk/chebi/ - Mandelic acid http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ - Mandelic acid EPA - Substance Registry Services - Mandelic acid Local: |
||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
White crystalline flakes | |
| ASSAY |
99.0% min | |
| MOISTURE |
0.1% max | |
| SULFATE |
0.05% max | |
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING |
| |
| HAZARD CLASS | ||
| UN NO. | ||
|
|
||
|
HAZARD OVERVIEW |
GHS (Globally Harmonised System) Classification: Not a dangerous substance. Potential Health Effects: Eyes - May cause eye irritation. Skin - May be harmful if absorbed through skin May cause skin irritation. Inhalation - May be harmful if inhaled. May cause respiratory tract irritation. Ingestion - May be harmful if swallowed. | |
| EC DIRECTIVES |
|
|
| HAZARD CODES |
|
|
|
RISK PHRASES |
|
|
|
SAFETY PHRASES |
||